Oncology is a branch of medicine that specializes in diagnosing and treating cancer. It deals with cancers and tumors and an oncology test which can help to know DNA changes present in cancer cells. Cancer may spread to any part of your body such as – brain, eye, head, neck, breast, stomach, liver, pancreas though it commonly moves into the bones, lungs or liver.
Oncologists specialize in managing drug treatments for people who are at early and advanced cancers that affect the muscles, organs, bones and connective tissue. But people who are in early-stage cancers may be treated with surgery or radiation therapy and may not need the care of an oncologist.
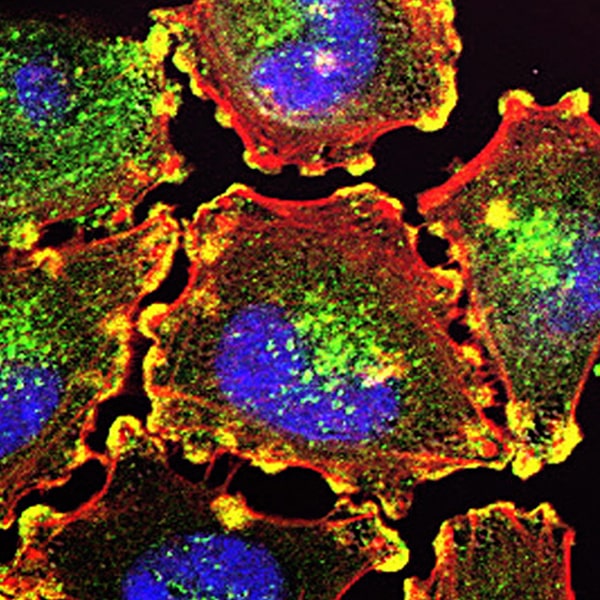
Oncologists need to diagnose cancer at first, which is usually done through biopsy, X-ray, CT scanning, endoscopy, MRI, ultrasound, PET scanning or other radiological procedures. Nuclear medicine can be used to diagnose cancer as blood tests or tumor markers.
Medical oncology is a core member of the MDT and provides cancer patients with a comprehensive approach to treatment and care. It ensures evidence-based, safe and affordable use of cancer drugs to preserve quality of life of cancer patients through the entire journey of cancer.
You can lessen the risk of having cancer with healthy choices such as maintaining a healthy weight, restricting the intake of alcohol and tobacco and protecting your skin.
The tumor marker tests use blood samples to detect the chemicals prepared by cancer cells. These tests do not help in diagnosing cancer as different healthy cells make these chemicals and some conditions which are not cancer lead to high levels of tumor markers.
These are broccoli, berries, grapes, walnuts, fruits, nuts and other vegetables.
Cancer cannot be passed down from parents to children. Certain genetic changes in tumor cells cannot be passed down. But a genetic change which increases the risk for cancer may be inherited when it is there in the egg or sperm cells of parents.
Visit and consult an Oncologist if you detect any symptoms of cancer!